C Programming - Rules
Every language specification defines its own syntax and rules. Before writing our first C program, let us understand its rules.
- Each instruction is written as a separate statement.
- Every C statement must end with a ';' (semicolon), this is known as the statement terminator.
- All keywords, syntax should be entered in small case letters.
- The statements in a program must appear in the same order in which we wish them to be executed, unless jumping statements are not used.
Hello World | First C Program
To write 'Hello World' which is our first C Program, we need a IDE (Integrated Development Environment), in this example we are using Turbo C++ IDE, which is originally from Borland.
Example 1.1: Write a program to print a Message "Hello World" 1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
printf("Hello World"); /* to print the statement */
getch();
}Code Explanation:
How to compile and run the program
There are 2 ways to compile and run the c program:
- By Menu: Click on compile menu and select compile option to compile the program. Then, click on run menu and select run option to run the program.
- By Shortcut key: Press ALT+F9 keys to compile the program and CTRL+F9 to run the program.
Hello World | VS Code
How to write 'Hello World' in Microsoft Visual Studio Code Editor.
Example 1.2: Write a program to print a Message "Hello World" 1
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
printf("Hello World"); /* to print the statement */
}Code Explanation:
How to compile and run the program
There are 2 ways to compile and run the c program, by menu and by shortcut key.
- By Shortcut Menu: Right click on the program window and select run code.
- By Shortcut key: Press CTRL+ALT+N it will compile as well as run the program.
How to accept input from user
Example 2: WAP to Input 2 numbers and find the sum. 1
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a, b, c;
printf("Enter 1st Number: ");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("Enter 2nd Number: ");
scanf("%d",&b);
c=a+b;
printf("Sum = %d",c);
}Enter 2nd Number: 20
Sum = 30
Code Explanation:
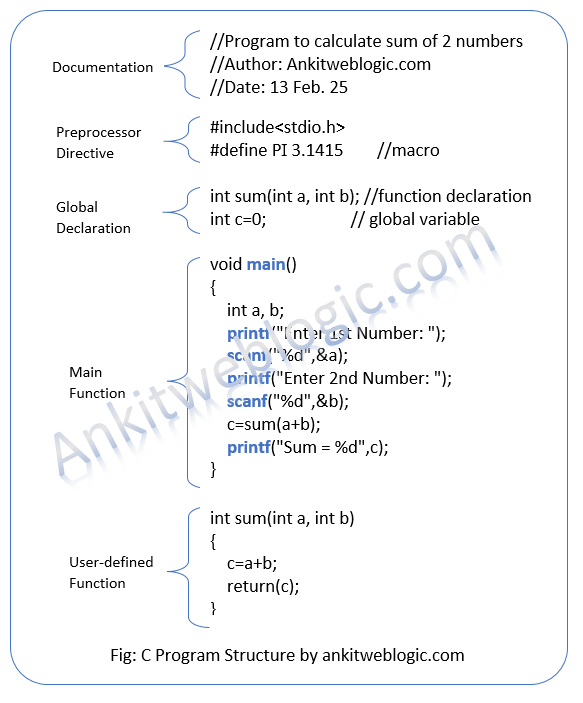
C Program Structure
Ad:

