C++ Inheritance
Inheritance is the process by which object of one class acquires the properties of another class. A derived class or subclass inherits all the attributes and behavior of the base class or super class, and may have additional ones as well.
Types of Inheritance:
class A class B:public A


class A class B:public A class C:public B
class A class B class C:public A, public B

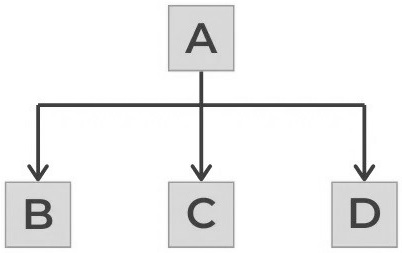
class A class B:public A class C:public A class D:public A
class A class B:public A class C:public A class D:public B, public C

Advantages of Inheritance
- Re-usability - we can reuse the features of existing class without redefining it.
- Save Time and efforts
Access Specifiers/ Access Modifier
In object oriented programming, we can control access to the data members and member functions through access specifiers. Each member, either data or function can have individual access specifiers. An access specifier is one of the following three keywords: private, public or protected.
Private members of a class are accessible only within a same class, from its member functions or from their friend function.
Protected members are accessible from members of the same class and from their friends, but also from members of their derived classes but in a same container.
Public members are accessible from anywhere, where the object is visible. They are like a global variable.
| Base class Modifier | Public derived | Protected derived | Private derived |
|---|---|---|---|
| Private | Not inherited | Not inherited | Not inherited |
| Protected | Protected inherited | Protected inherited | Private inherited |
| Public | Public | Protected | Private |
Ad:

